Diecast vs Resin Models What’s the Difference
The world of model collecting is filled with passion and precision, and at the heart of this hobby are the models themselves. Among the most popular are diecast and resin models. These meticulously crafted replicas of vehicles, aircraft, and other objects offer a unique glimpse into the world of miniature craftsmanship. Choosing between diecast and resin can be a pivotal decision for any collector, as each type presents its own advantages and disadvantages. This guide delves into the key differences between diecast and resin models, exploring five critical factors to help you determine which type best suits your collecting preferences and investment goals. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for making informed decisions, whether you’re a seasoned collector or just starting your journey into this fascinating hobby.
Material Composition Diecast vs Resin
The primary difference between diecast and resin models lies in their materials. This foundational aspect significantly impacts various characteristics, including weight, detail, and overall feel. Diecast models are typically made from a zinc alloy, often combined with other metals like aluminum or copper. This alloy is injected into molds under high pressure, a process that allows for intricate designs and robust structures. Resin models, on the other hand, are constructed from a polymer-based material. This material is a type of plastic that can be molded with exceptional detail, offering flexibility in design and production. The composition of these materials directly affects their physical properties, influencing everything from the model’s weight and durability to the level of detail achievable during manufacturing. Thus, the material composition becomes a key factor in evaluating which type of model aligns best with your collecting objectives.
Diecast Metal Alloy Explained

Diecast models get their name from the process used to create them, where molten metal is ‘die-cast’ into molds. The typical metal alloy used in diecast models is a zinc-based alloy. This alloy, often called Zamak, is a combination of zinc, aluminum, magnesium, and copper. The specific proportions can vary depending on the manufacturer and the desired properties of the model. This alloy offers an excellent balance of strength, durability, and ability to capture fine details. The weight and solid feel of a diecast model are a direct result of this metal composition, contributing to a premium feel that many collectors appreciate. The metal’s inherent properties also allow for high-pressure molding, which results in detailed and robust models.
Resin Plastic Composite Explained
Resin models are made from a liquid polymer that hardens when exposed to a catalyst or specific curing process. This composite material allows for very intricate and delicate detailing. The resin material is poured into molds, where it hardens to form the model. The nature of resin allows for greater design flexibility and can accommodate complex shapes and fine details that might be challenging with diecast metal. Resin is a type of plastic composite, offering a lighter weight compared to diecast, making it easier to handle and often resulting in a more delicate appearance. This characteristic also affects how the models are painted and finished, allowing for a wider range of effects and finishes.
Production Process
The production process plays a significant role in determining the final quality, detail, and cost of diecast and resin models. Each method has its unique advantages and limitations, influencing the types of designs and features that can be incorporated. Understanding the manufacturing process provides insight into why certain models may be priced differently or exhibit particular characteristics. This understanding helps collectors appreciate the craftsmanship involved in creating these miniature replicas and aids in evaluating the overall value and quality of each model.
Diecast Production Process
The diecast production process starts with creating detailed molds, often made from steel. Molten metal alloy is then injected into these molds under high pressure. This high-pressure injection ensures that every intricate detail of the model is captured. After the metal cools and solidifies, the models are removed from the molds, trimmed, and finished. This process allows for high-volume production, leading to cost-effective models. The die-casting method is particularly suitable for creating durable, weighty models. The nature of the process also ensures that the models are relatively resistant to warping or deformation, offering a level of consistency and quality control that is highly valued in the mass-production of model cars.
Resin Production Process
Resin model production typically involves pouring liquid resin into molds. These molds are often made from silicone or other flexible materials, which allows for intricate details. The resin is then cured, usually through a chemical reaction that hardens the material. This process is slower than die-casting, making it more suitable for limited production runs. Resin models can be produced with remarkable detail, as the molds capture every nuance of the original design. The process is also more adaptable for customization. Post-production, resin models often require hand finishing and detailing, adding to the exclusivity and often the higher cost of these models. This hand-finishing results in models with a very high level of detail, which collectors appreciate.
Detail and Accuracy
Detail and accuracy are paramount for collectors, as they determine the model’s realism and aesthetic appeal. Both diecast and resin models have their strengths in this area, influenced by their production methods and the materials used. The level of detail achieved can significantly impact a model’s value and desirability. Understanding the nuances of detail in each type of model can help collectors appreciate the craftsmanship involved and make informed choices. This allows collectors to appreciate the nuances of each model and select those that best reflect their standards for accuracy and detail.
Diecast Detail Advantages
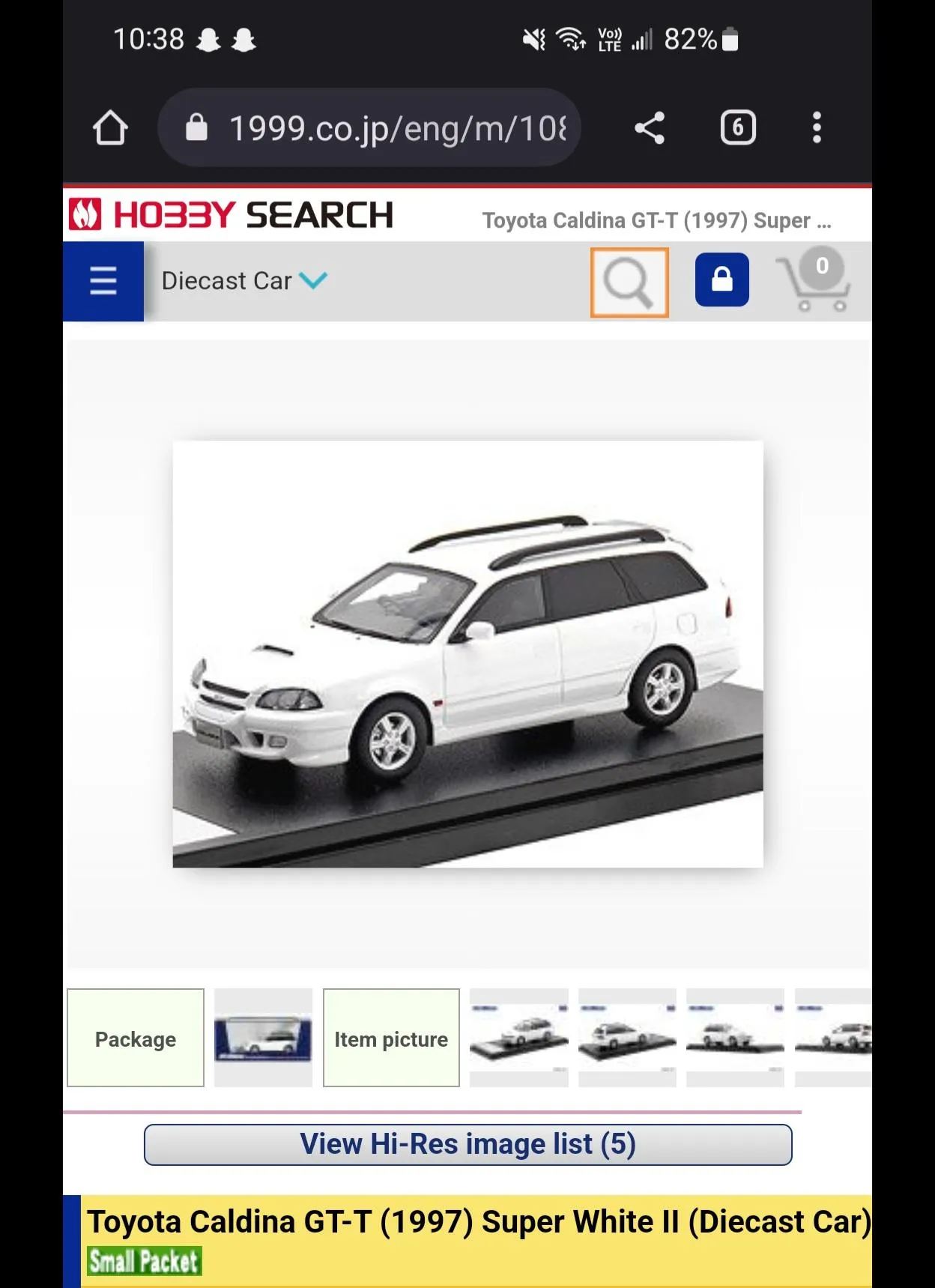
Diecast models often excel in capturing broad details and structural elements. The die-casting process allows manufacturers to replicate intricate designs with precision. This is particularly noticeable in the robust chassis, the detailed engine components, and the overall build quality of the model. The use of metal provides a solid base for adding detailed features. Diecast models often include functional parts, such as opening doors, hoods, and trunks, which enhance the realism and interactivity. The ability to use multiple materials in diecast models means that manufacturers can incorporate different textures and finishes, further enhancing the detail and realism. These factors combined offer models that are not only visually appealing but also durable and long-lasting.
Resin Detail Advantages
Resin models often have an advantage in terms of fine detail, allowing manufacturers to create more intricate and delicate features. The resin molding process allows for finer lines and more precise details. This level of detail is particularly beneficial in replicating complex body shapes, intricate grilles, and detailed interior elements. Resin models are frequently used for high-end, limited-edition models where the utmost accuracy is prioritized. Hand-finishing and detailing are common in resin models, with skilled artisans adding tiny details that enhance realism. This level of customization is particularly beneficial in creating models that are visually stunning and unique.
Durability and Weight
Durability and weight are critical factors that influence a model’s longevity, handling, and overall feel. These characteristics are primarily determined by the materials used in construction. A model’s ability to withstand wear and tear, as well as its perceived quality, is significantly impacted by these features. Collectors often consider durability and weight when deciding between diecast and resin models, as these factors affect the model’s investment value and the enjoyment derived from handling the miniature replica.
Diecast Durability Features

Diecast models are known for their superior durability, largely due to the metal alloy used in their construction. The zinc-based alloy provides excellent resistance to impact, making these models less prone to damage compared to their resin counterparts. The weight of the diecast models also adds to their perceived quality and stability. This weight helps keep the model grounded and makes it feel more substantial when handled. The robust nature of diecast models makes them suitable for display and handling. Their resilience to everyday wear and tear contributes to their longevity and investment value.
Resin Durability Characteristics
Resin models are generally more delicate than diecast models, making them more susceptible to damage from drops or impacts. The resin material can chip or crack under pressure, requiring careful handling and storage. However, resin’s flexibility allows for complex shapes without the risk of cracking or warping. While resin is less durable than diecast, it offers advantages in detail and design flexibility. Collectors often display resin models in protected environments to minimize exposure to potential hazards, ensuring the models remain in pristine condition. Proper care and handling are essential to preserve the intricate details and aesthetic appeal of resin models.
Cost and Availability
The cost and availability of diecast and resin models vary considerably, influenced by their production methods, materials, and target market. These factors play a key role in determining which type of model is more accessible to collectors. Understanding the cost implications and availability patterns is essential for collectors to manage their budgets and source models that match their interests. These considerations affect the feasibility of collecting certain models. This helps collectors to make informed choices about their acquisitions, aligning with their financial resources and collecting objectives.
Diecast Cost Factors

Diecast models are generally more affordable due to their mass-production capabilities. The die-casting process allows manufacturers to produce large quantities efficiently, reducing the per-unit cost. The availability of diecast models is typically widespread, with a vast selection available in hobby shops, online retailers, and department stores. However, the cost of diecast models can vary based on factors. The complexity of the design, the level of detail, and the brand’s reputation influence the price. Limited-edition diecast models or those with premium features may command higher prices. The mass-production nature of diecast models makes them more accessible to a broader audience.
Resin Cost Considerations
Resin models are typically more expensive than diecast models, mainly because of their production methods, which often involve hand-finishing and limited production runs. The resin process is labor-intensive. This increases the overall cost. Resin models are often available in limited quantities. This exclusivity can drive up their value and appeal to collectors seeking unique pieces. The price of resin models also reflects the level of detail, the brand’s reputation, and the scarcity of the model. These factors contribute to a higher investment, making them attractive to discerning collectors. The limited availability and high level of detail are key factors that drive up the cost of these models, adding to their allure for collectors.
Collecting and Investment Potential
The collecting and investment potential of diecast and resin models vary depending on factors like rarity, historical significance, and market demand. Models can be viewed as investments and the materials and craftsmanship affect the long-term value of these miniature replicas. Understanding the market trends and evaluating the potential for appreciation is crucial for collectors aiming to build a valuable collection. Collectors should consider several factors before investing in these items. Careful evaluation of the model, market analysis, and a keen understanding of collecting trends are crucial for achieving good investment results.
Both diecast and resin models have the potential to appreciate in value over time, with rarity being a key driver of investment returns. Limited-edition models or those depicting significant vehicles often command higher prices in the secondary market. Collectors should research the market trends, track the prices of similar models, and consider the demand for certain brands and types of vehicles. Some brands have a higher reputation than others. The condition of the model is a critical factor. It influences its investment potential, so models in pristine condition are highly sought after. With the right research and attention, both diecast and resin models can be valuable additions to any collection.
